
Spacers
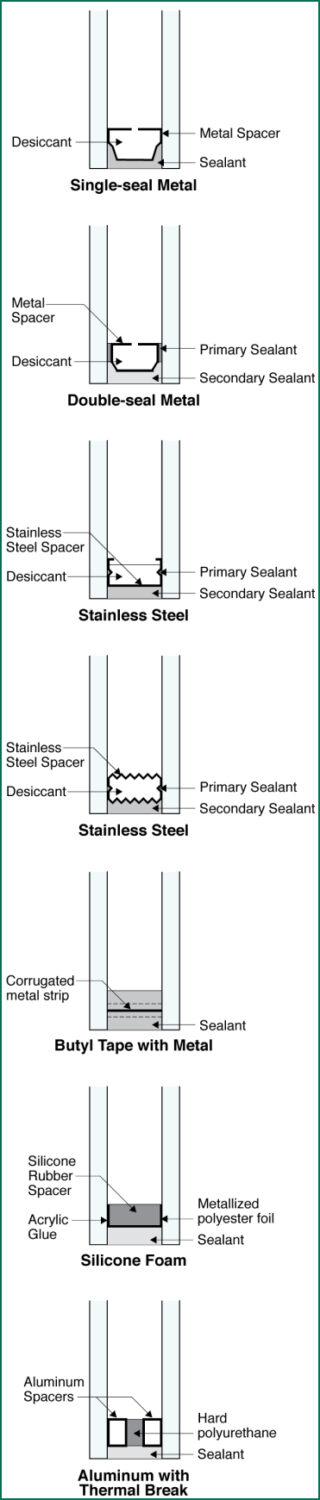
Spacers separate multiple panes of glass in a window and maintain the space between them. Spacers and the sealants used to hold them in place are referred to as spacer systems, and efficient ones help deliver the benefits consumers want:
- They seal the space between the glass panes to avoid fogging and prevent efficiency-boosting gases from leaking out
- They expand and contract along with the rest of the window
- Provide a gas-tight seal that prevents the loss of any special low- conductance gas in the air space
- In cold climates, spacer systems can reduce heat loss, condensation, and water damage
Spacer Types
- Non-metallic spacer systems are most efficient in blocking heat and cold transfer and reducing condensation. Their flexibility allows them to expand and contract along with the rest of a window, which protects the seal from cracks.
- Warm-edge spacer systems block heat and cold from passing through a window by blending metallic and non-metallic materials. This also cuts condensation.
- Metal spacer systems are common, but heat and cold can pass easily through them. This makes it more difficult for heating and cooling systems to maintain interior temperatures, and risks condensation.